WORK and ENERGY
PURPOSE:
To study the relationship between work, potential energy, and
kinetic energy
MATERIALS:
CBL with motion probe
Pasco cart
Pasco track
Vernier "PHYSICS" suite of
programs
TI-83
DIAGRAM:
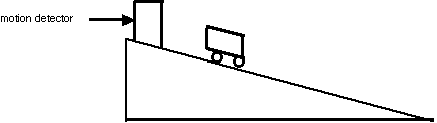
PROCEDURE:
- Connect the motion probe to the sonic port on the CBL.
Turn on the Vernier PHYSICS program in your TI-83.
- Set the probes for one motion probe
- Collect data using the time graph option and the live display
option.
- Enter time between samples as 0.01 and number of samples as
80.
- Set the graph options on the program as ymin=0, ymax=1, yscl=0.1.
- Place the sonic motion probe at the top of the ramp and place
the Pasco cart 35cm. away. (see diagram above ) Release the cart
and let it roll down the ramp. Stop the cart at the bottom being
careful not to get your hands between the cart and the motion detector as it scans
the cart's motion.
- Go to the view graph option in the program. Find
and record the time and distance values for the cart at the start
and the end of its run.
- Repeat this experiment two more times
changing either the mass of the cart or the angle of the ramp.
Your data should include the mass of the cart and the angle for
each trial. Organize your data in a table format.
CALCULATIONS
Calculate the following values making sure to include formulas with
units for all calculations. Make sure your answers reflect the
correct number of significant figures.
- Change in time
- Distance traveled
- Average velocity
- Final velocity (assume constant acceleration)
- Potential energy at the top of the run (use length of run
and Q )
- Kinetic energy at the end of the run
- Work done by gravity
- Percent difference between potential energy at the top and
the kinetic energy at the end of the run
Written by Art Brown, July 1997

